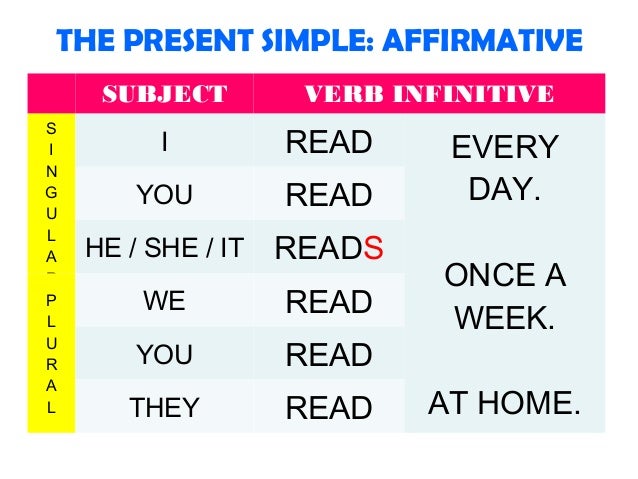
El Presente Simple es un tiempo verbal que se utiliza para describir acciones habituales que suceden con cierta frecuencia y no hace referencia a si está ocurriendo en el momento actual.
Por ejemplo las cosas que realizamos todos los días (caminar, estudiar, almorzar, leer, salir...). En Inglés existe una regla, y es que cuando se habla de la tercera persona, se le agrega s al final del verbo, si la oración es afirmativa. Es decir que cuando se hable de (el, ella o un objeto o cosa, /he, she, it) se le agrega s al final del verbo si lo que se dice es cierto. Por ejemplo:
I speak English
He speaks English
Primer ejercicio para completar y enviar.
Completa cada oración con el verbo que esta en paréntesis, teniendo en cuenta las reglas anteriormente mostradas.
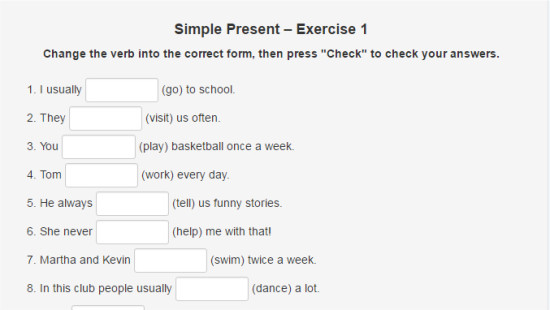
Segundo ejercicio para completar en linea, no necesita ser enviado.
Abre el siguiente link Exercise #1 y teniendo en cuenta las reglas del presente simple en afirmativo, selecciona uno de los verbos que te muestran. Al final, le das un clic a: Check answers y podrás ver la corrección de cada oración del ejercicio.
-Comenta aquí debajo: (esto es parte de la participación)
¿Para qué nos sirve el presente simple en la vida diaria?
¿Crees que es importante éste tema? ¿Por qué?